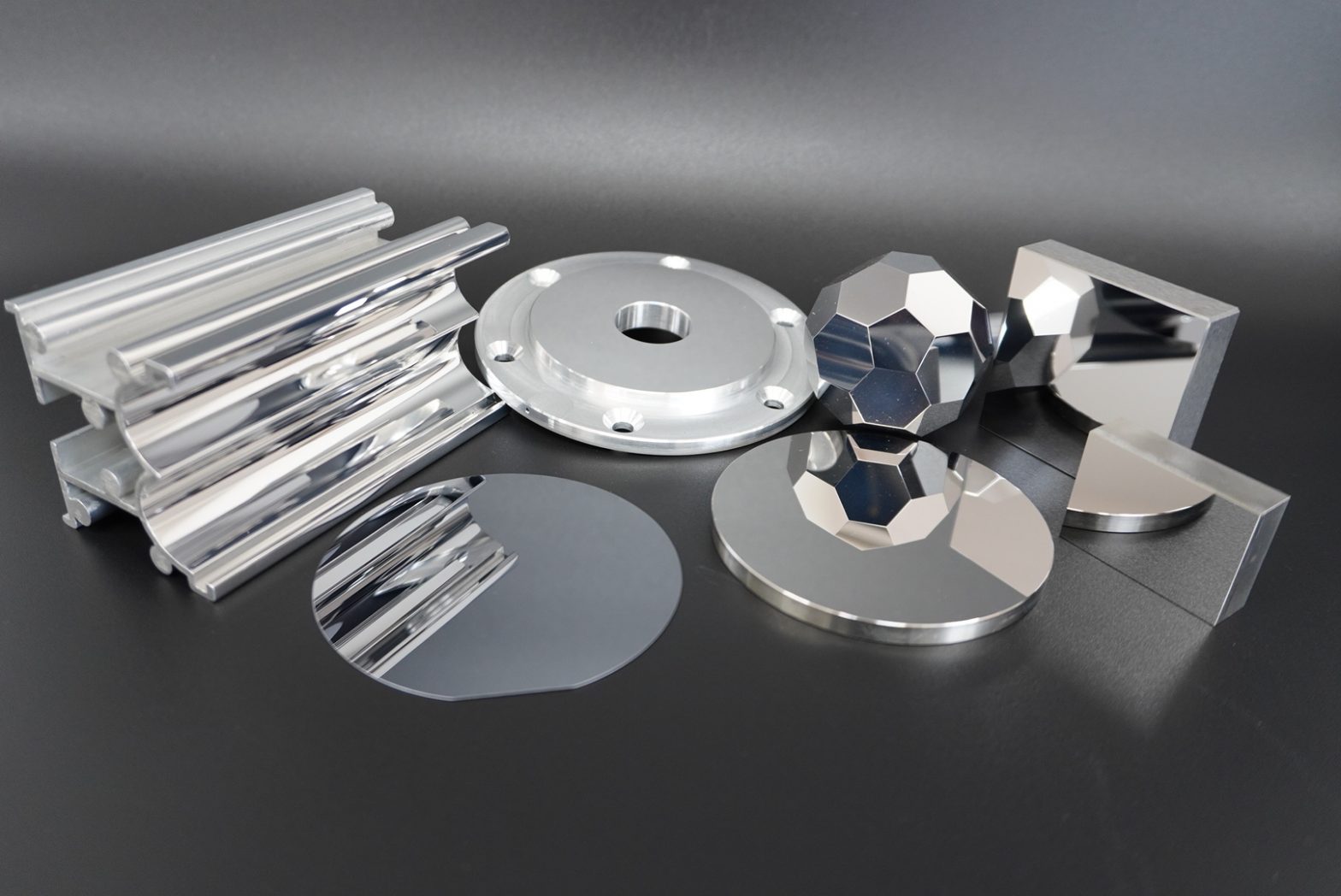
Polishing service
Here is some basic knowledge about polishing technology and some applications for our service.
What is polishing?
Polishing is a process that uses abrasive grains (small hard particles) to remove unevenness on the surface of a product.
There are various types and materials of abrasive grains used in polishing, but by selecting the abrasive grains and processing method according to the object to be processed, it is possible to adjust in μm (micrometer), that is, in micron units, so the product It is used in the final process of processing.
The target materials are generally metals and ceramics for electronic parts and molds that require high precision, glass and various crystal materials used for optical equipment, resins and plastics, etc., but TDC processes all kinds of materials. can accept
What is the difference between polishing and grinding?
“Polishing” and “grinding” are similar in the point; they remove the surface of the product.
Therefore, both are sometimes used interchangeably, but in some cases, we are going back and forth between cutting, grinding, and polishing processes for one product to achieve the required shape and accuracy.
Grinding is an abrasive machining process that uses a grinding wheel as the cutting tool and removes saw marks and levels and cleans the specimen surface
On the other hand, polishing uses free abrasives called slurry and removes the artifacts of grinding but very little stock and because of that, there is less damage to the object (processing stress and creation of a processing alteration layer), and therefore, higher accuracy can be achieved…
We select the appropriate polishing / grinding method to meet the required accuracy and processing purpose.
various polishing methods
There are various polishing methods depending on customers’ needs.
lapping
Lapping is a machining process to use lapping machine. which two surfaces are rubbed together with an abrasive between them, by hand movement or using a machine .In double-sided wrapping, the product is sandwiched between two flat plates (surface plates) and single-sided wrapping is a processing method in which the product is placed on a surface plate and pressure is applied from above to rub the product against the abrasive containing abrasive .It is applicable for things where flatness is extremely important, such as lens manufacturing and molds, blades, because lapping can produce extremely flat surface precisely.
polishing
It is similar to lapping in that it uses lapping machines and abrasives. However, polishing differs in that it uses soft materials such as cotton and felt. In addition, it is often used in the final process (polishing, mirror finishing, etc.) that requires a delicate finish by selecting the type of surface plate (pad) and the type of abrasives.
grinding
Grindstone is a processing method in which the grindstone is fixed and moved while being applied to the product, or the product is applied to a rotating grindstone to polish the surface. Sharpening scissors or knives with a whetstone is also one of example of grinding. Generally, it is called “polishing”, but strictly speaking, it is called “grinding”.
barrel polishing
Barrel polishing is used is to polish the surface by putting products and polishing stones, and a polishing agent called compound, which has a cleaning and smoothing action, in a large container and vibrating or rotating it. The advantage is that you can polish a large number of products.
cutting
Cutting is a processing method that cuts out the shape you want to finish rather than finishing the surface cleanly, and the process is different from polishing.
Since it is a machining process, it is generally applied immediately after the product is designed, and in some cases polishing is performed after cutting.
There are two types of cutting: roughing and finishing. In finishing, the cutting depth and pitch are finely adjusted, so the surface can be finished to a certain degree of beauty.
coated abrasive
Coated abrasive means polishing with sandpaper. It is one of the fixed abrasive grain processing methods, in which the abrasive is evenly distributed on the surface of cloth or paper. It is placed in a ring shape on a so-called polishing belt and rotated and polished while applying the product to this.
electrical discharge machining
In electrical discharge machining, metal is processed using “electrical energy”. As an image, it can be said that it is a “processing method to extract” rather than cutting out.
It is a machining method in which an arc discharge is passed between the electrode and the workpiece, and part of the product to be machined is removed by the heat of the discharge.
Since the approach is completely different from other machining methods, it is often used for machining hard materials that cannot be removed by other removal machining.
electropolishing
Electropolishing is a method of immersing a product in an electrolytic solution and applying a direct current to obtain a polishing effect. This method is used when it is difficult to handle with other polishing methods, but it also has the disadvantages of limited metals that can be handled and higher cost.
Types of familiar polishing processes
Polishing processing is not limited to processing using factories or dedicated machines and equipment.
We will introduce familiar polishing that exists in everyone’s life.
Whetstone polishing (manual work)
Polishing using whetstones is familiar to us. An example of this is whetstone polishing of kitchen knives. Although precision is generally not required, the whetstone used and the sharpening method change according to the workpiece.
Polishing with sandpaper
If you’ve ever done any DIY or craft, you’ve probably used sandpaper before. This sandpaper is also one of the excellent polishing methods.
Lens polishing
Camera and microscope lenses are also manually polished in the final manufacturing process. It is one of the polishing processes that we can feel familiar with.
For a detailed explanation of the types of polishing, please refer to the “Types of Polishing” page.
What are abrasive grains?
Abrasives are hard particles used for polishing. In other words, it is a “blade” that scrapes and polishes the object, and the major difference from cutting tools is that the blade grows and changes while repeating fine crushing.
Abrasive grains are broadly divided into “general abrasive grains” and “superabrasive grains”, and general abrasive grains are further classified into alumina and silicon carbide.
In general, alumina-based abrasive grains (alundum) are used for steel and hardened steel, and silicon carbide-based abrasive grains (carborundum) are used for stone and cast iron.
Specific abrasive grains are as follows.
- A (Brown Alumina)…Alumina abrasive grains called ordinary A abrasive grains. Used for general steel and free grinding, it is generally sharper than C abrasive grains, but it is softer than C abrasive grains, and C abrasive grains are superior in friability.
- WA (White Alumina): High-purity alumina, which is the most commonly used abrasive for general whetstones. Used for general hardened steel, alloy steel, tool steel, stainless steel, etc.
- HA (Pulverized Alumina)…Since it is made of single crystal, it is difficult to crush and suitable for precision grinding. Used for precision polishing of alloy steel, tool steel, stainless steel, etc.
- PA: (Pink-colored alumina) …Higher toughness than WA, and excellent shape retention. It is used for alloy steel, special steel, tool steel, and gear grinding.
- C: (Black Silicon Carbide)…It is called ordinary C abrasive grains and is used for non-ferrous metals and cast iron. It is harder than A abrasive grains and has excellent friability.
- GC: (Green Silicon Carbide)…High-purity C abrasive grains. It is used for cemented carbide and special cast iron.
Polishing procedure
The polishing process is roughly divided into” rough polishing, “” medium polishing, “and” finishing“.
In rough polishing, we use coarse abrasives to remove large irregularities, and in medium polishing, the surface is smoothed with smaller abrasives than rough polishing. The process of rough polishing to medium polishing is in charge of the work of removing a large amount of polishing allowance and creating the shape we need.
In the finish, the surface evened by medium polishing is polished with finer abrasive grains so that it becomes mirror-surface. Make fine adjustments to the accuracy. In mirror finishing, the amount of removal as a polishing allowance is very small because it is carefully polished little by little, but it is an important process for achieving high accuracy.
1. Base
For the undercoat, a coarse whetstone is used to remove large irregularities and foreign matter on the surface. The groundwork is a very important process in polishing, and it affects the final finish.
Select a coarse whetstone for polishing. Numbers are assigned according to the grain size of the abrasive grains, and the smaller the number, the larger the abrasive grains and the coarser the whetstone.
At the groundwork stage, rather than finely aligning the surface, it is a process of boldly scraping.
2. Smoothing
This process uses a finer whetstone than the whetstone used for the groundwork to further smooth the surface from which irregularities and foreign matter have been removed.
If the surface of the product is flat on the base, the process is not that difficult.
Due to the use of high number and fine whetstones, the surface will be almost flat by the time the smoothing process is finished.
3. Polishing
It is a process to make the flattened surface glossy and make the product surface look even more beautiful.
In the process of groundwork and smoothing, the image is to flatten the surface of the product, add a gloss to it, and remove dirt from the surface. Therefore, the whetstone to be used is selected to be finer than that used in the smoothing process.
There are also processing methods that intentionally scratch the surface, such as vibration polishing and hairline processing.
4. Mirror Finish
Literally, it is a polishing process that gives the surface of the product a mirror-like luster.
In addition to carefully polishing with a higher-numbered whetstone with finer-toothed whetstones, it is also possible to achieve finer finishes by gradually increasing the number of whetstones.
“Buffing”, which uses abrasives and abrasives on soft materials such as cloth, is sometimes used.
TDC’s polishing technology
In TDC’s precision polishing and lapping, the workpiece and surface plate both rotate respectively. As it approaches the finish, the abrasive (slurry) is changed to smaller abrasive grains. We explain TDC’s polishing procedure with a picture.
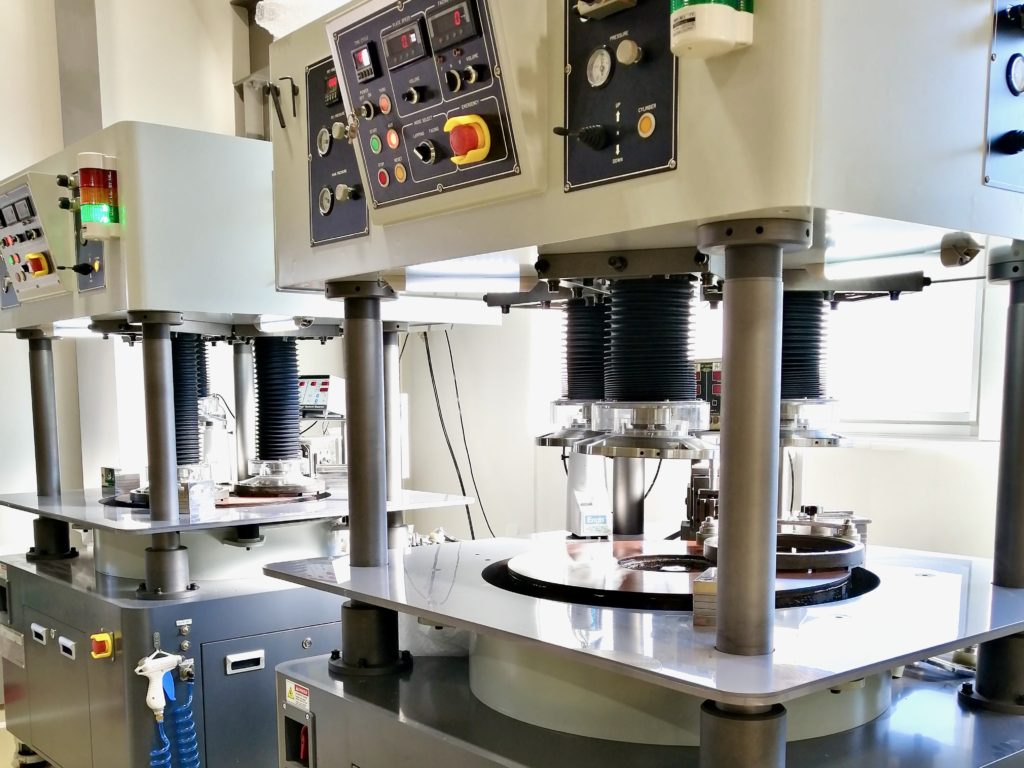
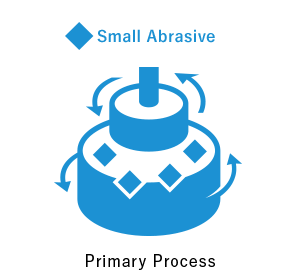
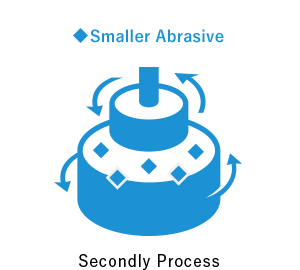
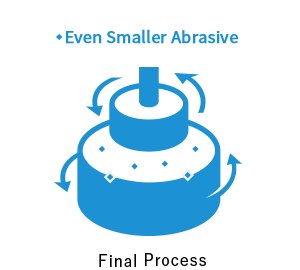

We offer the world’s highest level of ultra-precision machining and ultra-precision lapping, such as surface roughness, parallelism, flatness, and dimensional accuracy.
Materials
| Metals | Stainless Steel / Superalloy / Copper / Titanium / Aluminum / Molybdenum / Tungsten/ Nickel / Tantalum etc. |
| Ceramics | Al2O3 / ZrO2 / SiC / Si3N4 / SiO2, Also Coating and Plating are acceptable |
| Crystalline Material | BK7/ Crystal/ PYREX/ Quartz / Si/ SiC /GaN/ Sapphire/LiTaO3/LiNbO3/ |
| Resin | Engineering Plastics / PEEK/ PMMA /PEFE |
Processing Achievement
φ100x5mmt
| Polishing | Lapping with GC | |
| Flatness | 0.1 μm | 1 um |
| Roughness(Ra) | 1 nm | Pear skin Finish/ Frost |
| Parallelism | 1 um | 2 um |
| Tolerance | ±0.5 um | ±1 um |
Applications
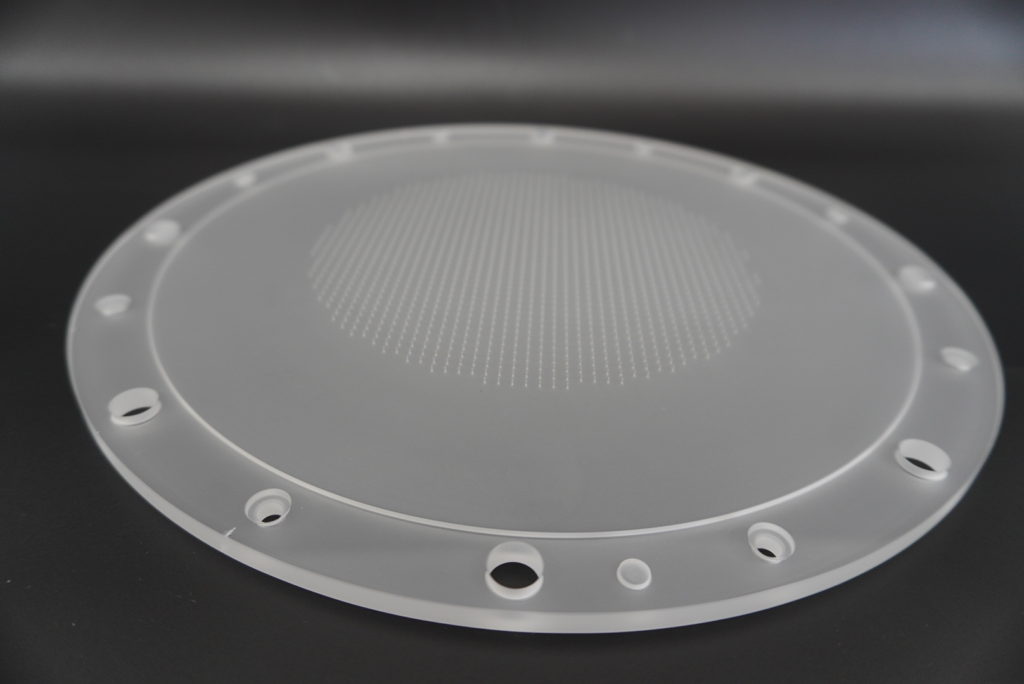
Wafer chuck plate, precision table
We process positioning plates and plates that require precision, which are used in semiconductor manufacturing equipment and precision measuring machines. It is possible to finish the flatness, parallelism, and dimensional tolerance with high accuracy, and to create the desired surface roughness such as smooth surface and satin ground.
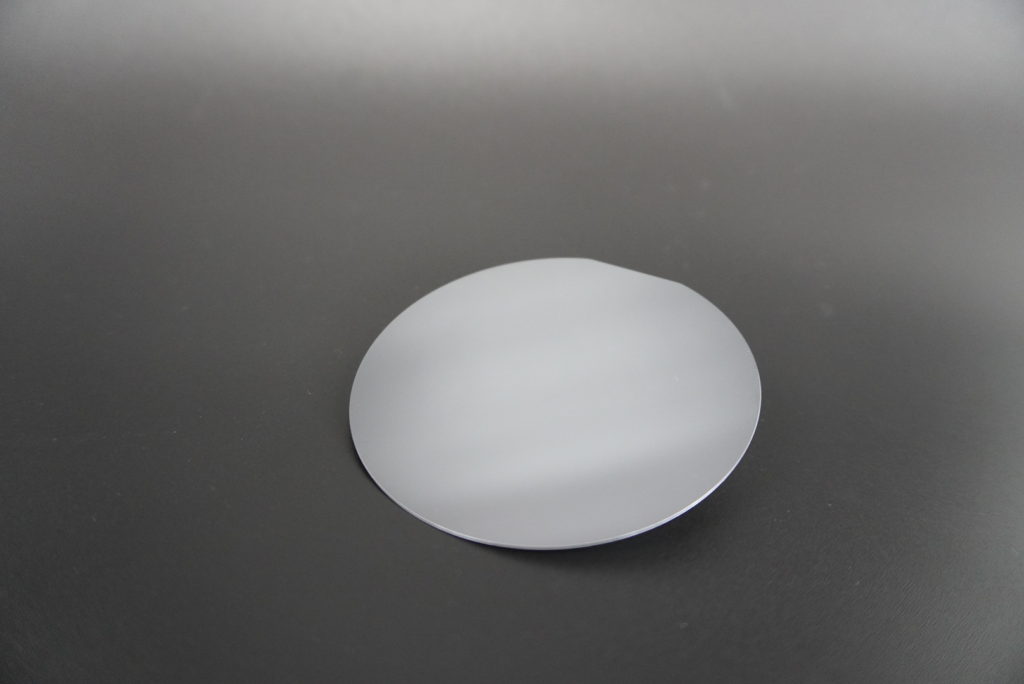

Various crystal wafers
We perform precision CMP and thin polishing of wafers made of various materials such as silicon, sapphire, SiC, and diamond. We support from 1 sheet to small lots for experimental research to mass production.

Shim
We manufacture shims that guarantee high accuracy such as ± 0.5 um and ± 1 um with thickness variations of 1 μm in the field where precise assembly is required, such as precision measuring machines, electronic devices, and medical devices,
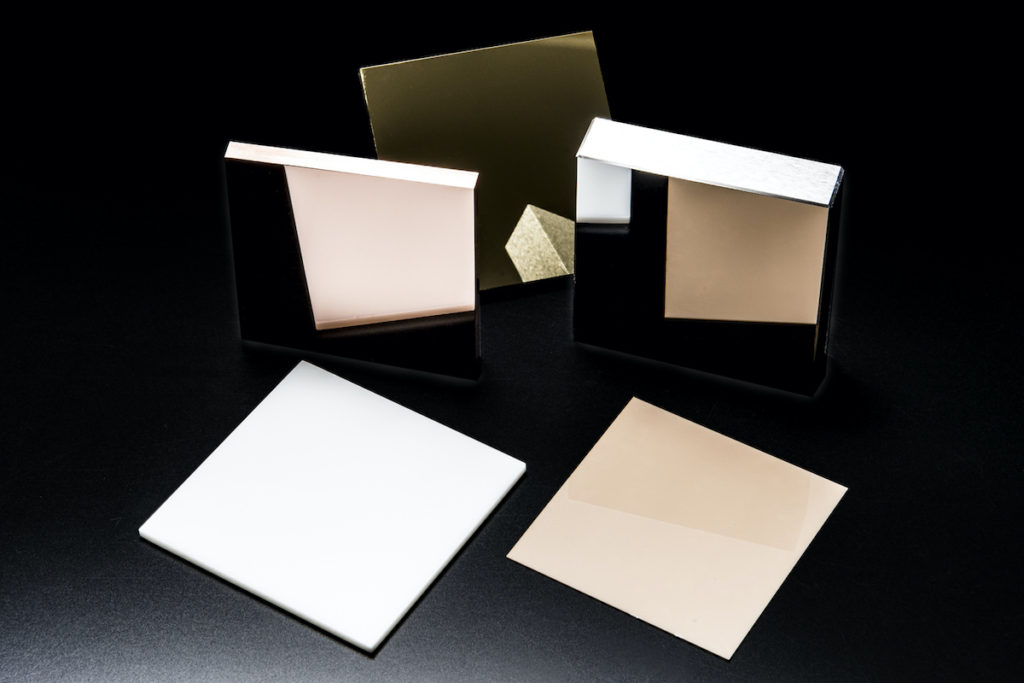

Test piece
Processing of test pieces used for friction and wear tests and tensile tests is also compatible with various materials. We also accept quick delivery.

Surface plate
We perform precision machining of surface plates used as reference planes in assembly and inspection that require an absolute flatness. In addition to stone surface plates and ceramic surface plates, we offer thermal spraying surface plates.
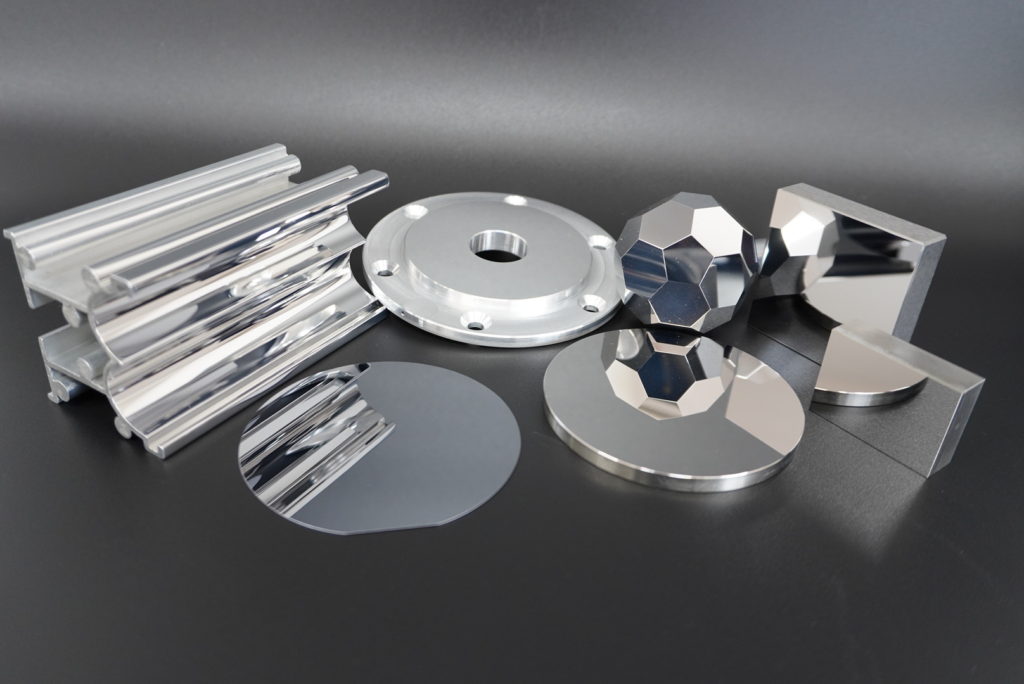

Mold
It is used in the production of various products such as plastic working, press working, and injection molding, and we perform precision polishing of dies where precision is extremely important. we handle not only flat surfaces but also complex shapes and uneven lens shapes.

Sphere
We also process spheres for high-precision bearings and measuring probes. Ultra-precision can be achieved even for spherical surfaces where sphericity and surface roughness are crucial.
Polishing Processing
Here is our manufacturing processing.
Feel free to send us the drawings for inquiry and we will support all processing.
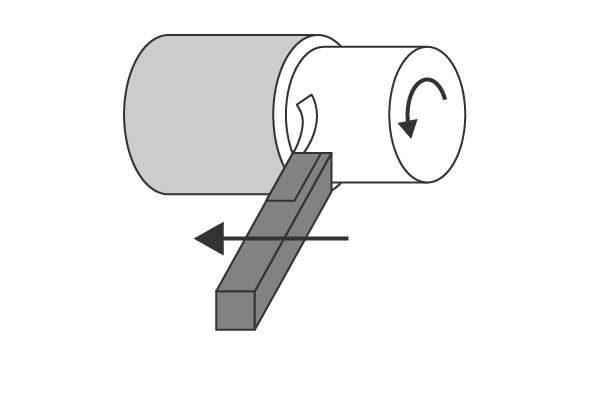
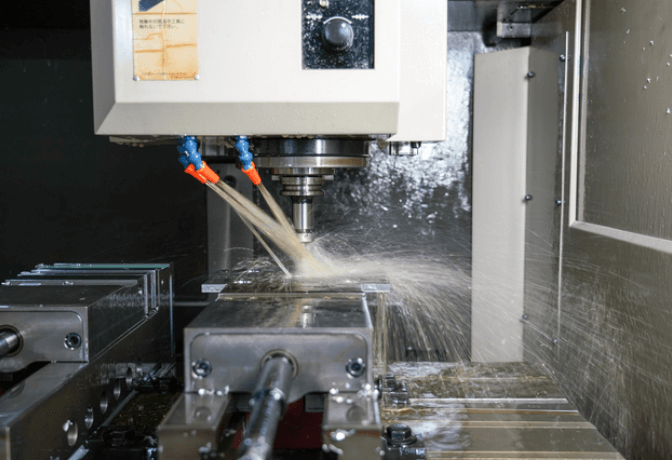
1.Cutting
Make the shape of a thing using a cutting tool such as cutting tools, drills, or end mills. We can change the shape quickly and greatly.
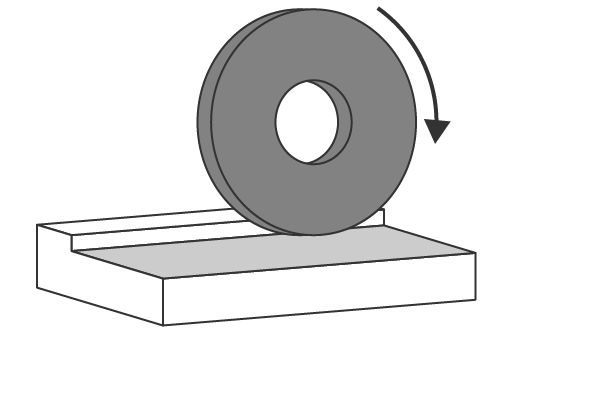
2.Grinding
Use fixed abrasive grains (grinding stones) to shape the object. Enable us to efficiently create the required dimensions, shape, and roughness.
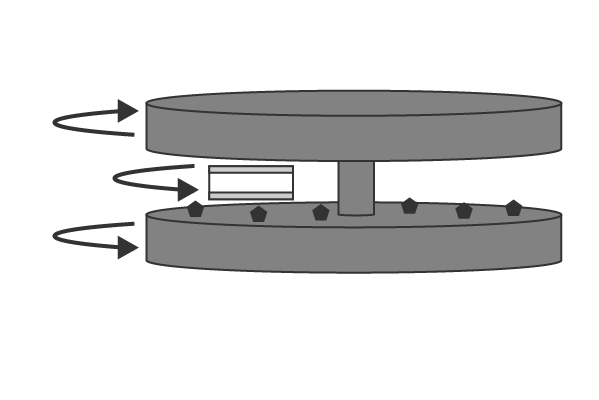
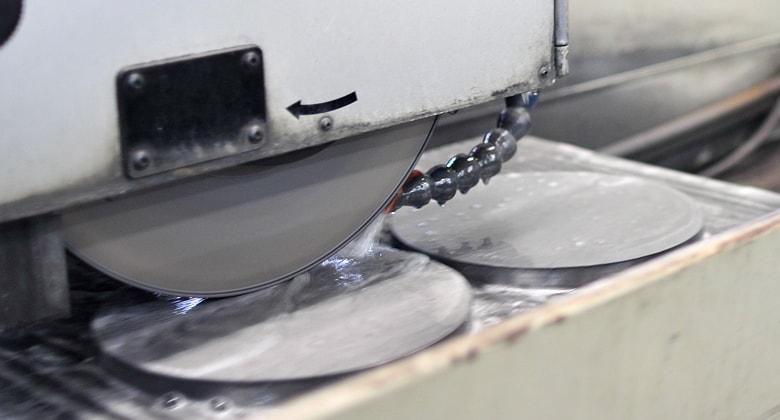
3.Polishing
By slightly polishing the object using free abrasive grains (slurry), we can finish with the specified tolerance, surface roughness, and shape accuracy.
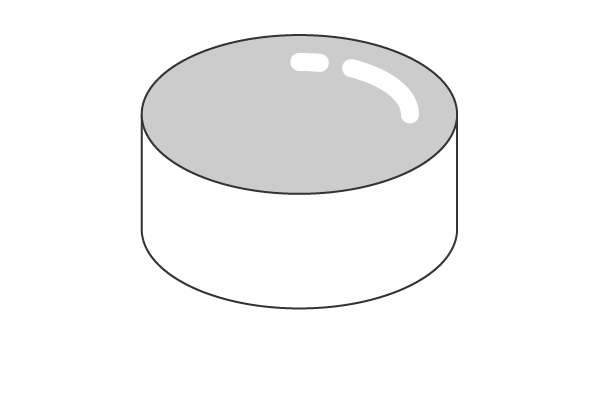
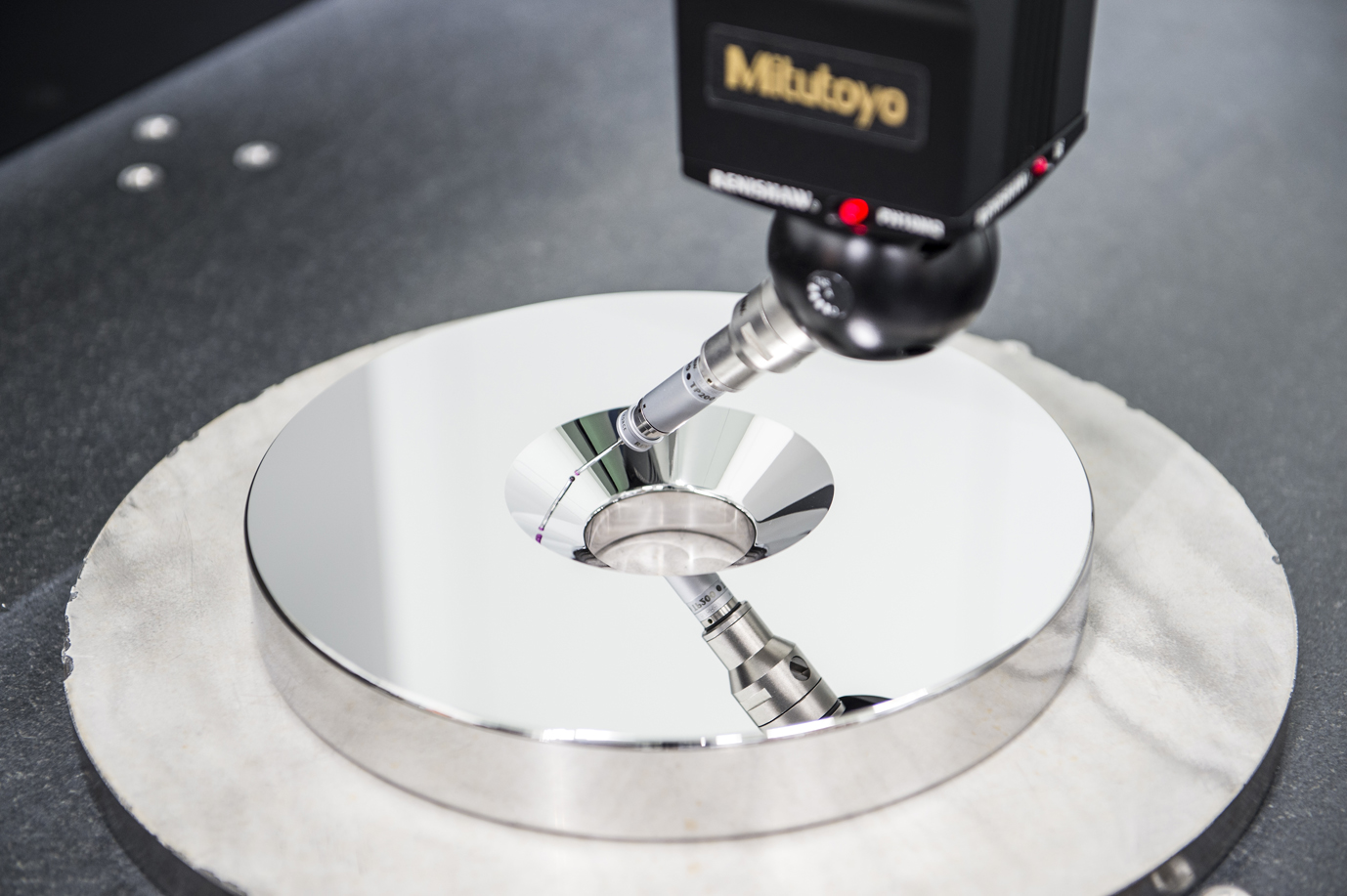
4.Inspection
Using the world’s highest level evaluation equipment, measurement is performed by professional staff in a measurement room at 20 ± 2 ° C and in a clean environment.
5.Cleaning
Ultrasonic cleaning is performed so that there are no visual stains or deposits.
6.Quality Assurance
Specialized staff check each final product one by one and carry out thorough quality control. We will deliver the inspection data as an attachment.
7.Shipping
TDC’s ultra precise lapping/polishing technology enables us to realize high precision manufacturing.
The ultra-precision polishing technology enables high-precision manufacturing in various elements.
- We deal with wide range of materials such as metals, ceramics, crystal materials, and resins in the size of □ a few micron to □ 800 mm.
- We realize ultra-precision polishing and ultra-precision lapping with surface roughness Ra1 nm and Rz4 nm for shapes such as flat surfaces, curved surfaces, and inner and outer diameters of cylinders.
- For other processing elements such as “parallelism 100 nm”, “flatness 30 nm”, “dimensional accuracy ± 100 nm”, “angle ± 3 seconds”, and “sphericity 50 nm” while clearing advanced “surface roughness”. High precision is possible.
- Our technology is used for cutting-edge technologies in various fields such as electronic components, semiconductors, optics, medical care, aviation, space, automobiles, and energy.
Regardless of the material and shape, we can handle precision processing by our polishing service.
Please feel free to contact us for more information.
Related page






