Invar/Super Invar
This page explains the features and applications of Invar/Super Invar, and examples of TDC processing.
Contents
What is Invar (Invar 36/FN36)?
Invar (Invar 36/FN36) is a low-expansion metallic material containing 36% nickel in iron. The name invar is derived from Invariable Steel (steel that does not deform), and it is also called “invar alloy” or “amber alloy” because it is also called amber in French.
In Japanese, it is also called “low thermal expansion alloy”, “invariant steel”, and “cast steel/forged steel”.
Components of Invar (Invar 36/FN36)
The components that make up Invar are as follows.
| component | composition ratio(%) |
| Ni | 35.0-37.0 |
| Fe | Bal (about65.0) |
| Mn | 0.60以下 |
| Co | 0.50以下 |
| Si | 0.40以下 |
| Cr | 0.25以下 |
| C | 0.20以下 |
| P | 0.025以下 |
| S | 0.025以下 |
Physical Properties of Invar (Invar 36/FN36)
The physical properties of Invar are as follows.
| Electrical resistivity | 75-85(μΩ・cm) |
| Young’s modulus | 140-150(GPa) |
| Rigidity modulus | 57(GPa) |
| Curie temperature | 276.7℃ |
| Brinell hardness | 160 |
| Elongation at break | < 45 % |
| resilience (20°C) | 140-150(J/cm2) |
| Poisson’s ratio | 0.22807 (=E/2G – 1) |
| Tensile strength | 450-590(MPa) |
| Density | 8,125(g/cm-3) |
| Linear expansion coefficient(20-90°C) | 1,2-2,0 x 10-6 K-1 |
| Thermal conductivity (23°C) | 13 Wm-1K-1 |
| Specific heat capacity | 510 JKg-1K-1 |
| Melting point | 1426℃ |
Characteristics, characteristics and properties of Invar
In general, metals have the property of expanding when heated and contracting when cooled.
However, invar remains almost unchanged at a specific temperature, and its coefficient of thermal expansion is less than one-tenth that of iron and nickel.
Other materials with low coefficients of thermal expansion include ceramics and tantalum, but the characteristics of invar are its electrical conductivity, elasticity, and the unique properties of a metal that can be welded or soldered. The point is that
In addition, Inver has the following features:
- Cheaper than tungsten etc.
- Boasts high toughness even in a low temperature environment of about -200°C
- Highly stretchable and ductile at room temperature, and highly workable
Substance with properties similar to invar
If you want to keep the coefficient of thermal expansion even lower than that of Invar, the above-mentioned “Super Invar” is useful, and if you want to combine it with glass, “42 alloy” or “Kovar”, which have a low coefficient of thermal expansion even at high temperatures, are useful.
What is Super Invar
Super Invar is a ternary alloy containing 32% nickel and 4% cobalt in iron. Its coefficient of thermal expansion is less than 1/100th of iron, which is even better than invar.
It is also called “super-normal steel”, “super-normal steel”, and “super amber”.
42 alloy
42 alloy is an alloy of iron mixed with 42% nickel.
It is a metal with a coefficient of thermal expansion similar to that of hard glass, and is used for electrodes of electronic parts and IC lead frames sealed with glass for hermetic protection.
The physical properties of 42 alloy are as follows.
| Density | 8.15(g/cm-3) |
| Melting point | 1430℃ |
| Electric resistivity | 0.635(μΩ・cm 20℃) |
| Thermal conductivity | 14.6 W/(m*K) |
| Thermal expansion coefficient | 30〜330℃ 45〜65 * 10-7/℃ |
| Magnetic transformation point | 330℃ |
Kovar
Kovar is an alloy of iron with 29% nickel and 17% cobalt.
Its coefficient of thermal expansion does not change over a wide temperature range, similar to that of silicate glasses and alumina ceramics.
It is an alloy that can be brought into contact with hard glass and ceramics, and is used for sealing and encapsulation.
The physical properties of Kovar are as follows.
| Density | 8.0(g/cm3) |
| coefficient of thermal expansion | 5.2(10-6 K-1 (25 – 200℃)) |
| Thermal conductivity | 17(W/Km) |
| electrical resistivity | 0.49(Ω mm2 / m) |
| Tensile strength | 55(Kg/mm2) |
| Hardness | 160(HV1) |
| Young’s modulus | 159(GPa) |
| yield strength | 270(MPa) |
| curie point | 435(℃) |
| specific heat | 0.46(J/gK) |
Applications of Invar
Due to its low thermal expansion coefficient and small dimensional change due to temperature changes, Invar is used in precision equipment and precision devices that need to avoid the effects of heat.
The main uses of Invar are as follows.
- Semiconductor manufacturing equipment
- Semiconductor exposure equipment
- optical device
- Manufacturing equipment
- Precision inspection equipment
- Various measuring and surveying equipment
- Low expansion side of bimetal
- shadow mask frame
- seismic activity detector
- Aerospace Molds for Composite Parts
- clock etc.
Machinability of Invar
Invar has a low thermal conductivity, and heat builds up in the material, making it prone to warping. In addition, because it is a sticky material, it is treated as a difficult-to-cut material that is difficult to process.
At TDC, we can process all types of invar, which is considered to be a difficult-to-cut material, with the polishing and grinding technology we have cultivated so far.
Please feel free to contact us if you have any problems with the processing that other companies have refused or the processing of Invar.
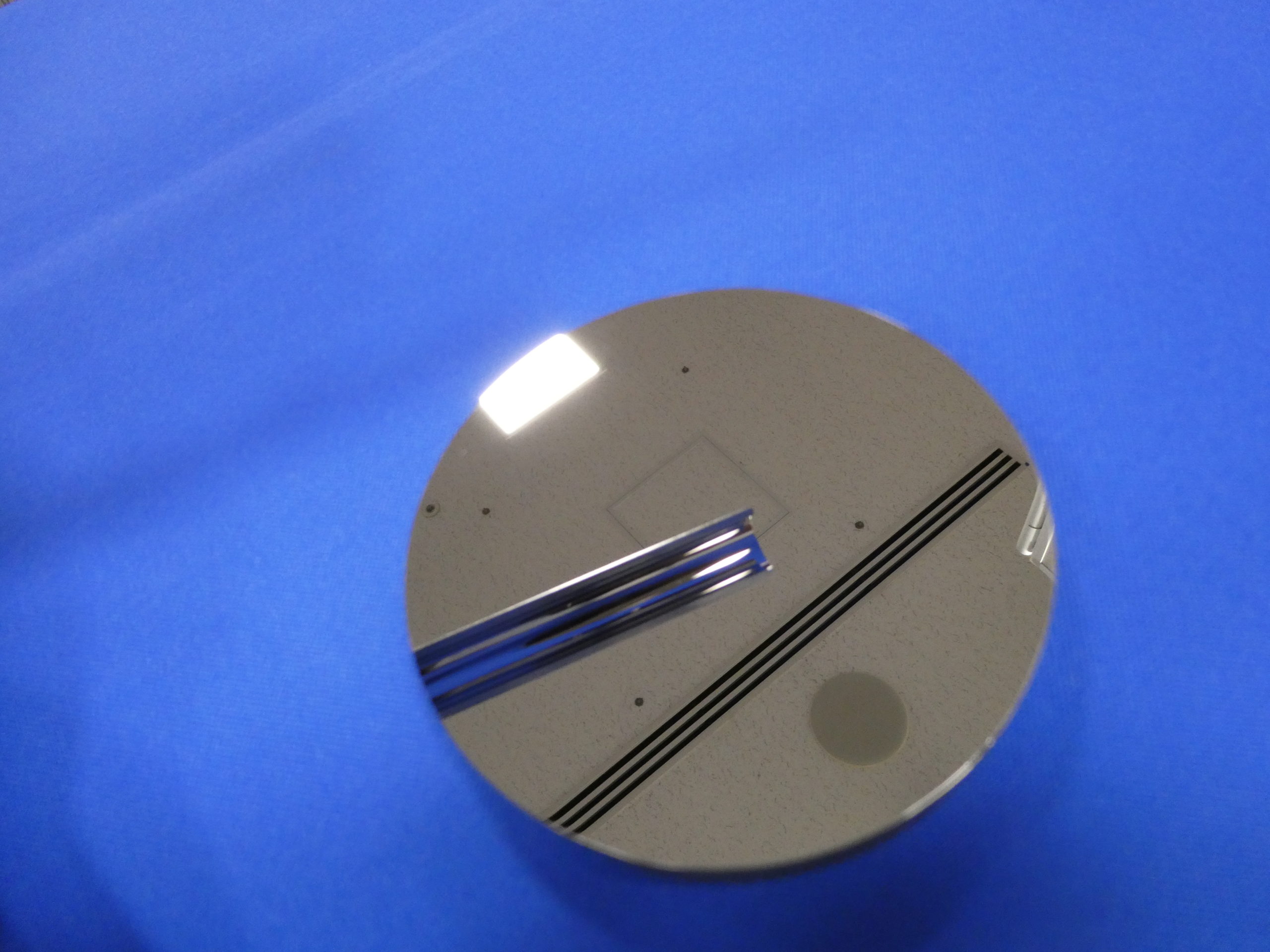
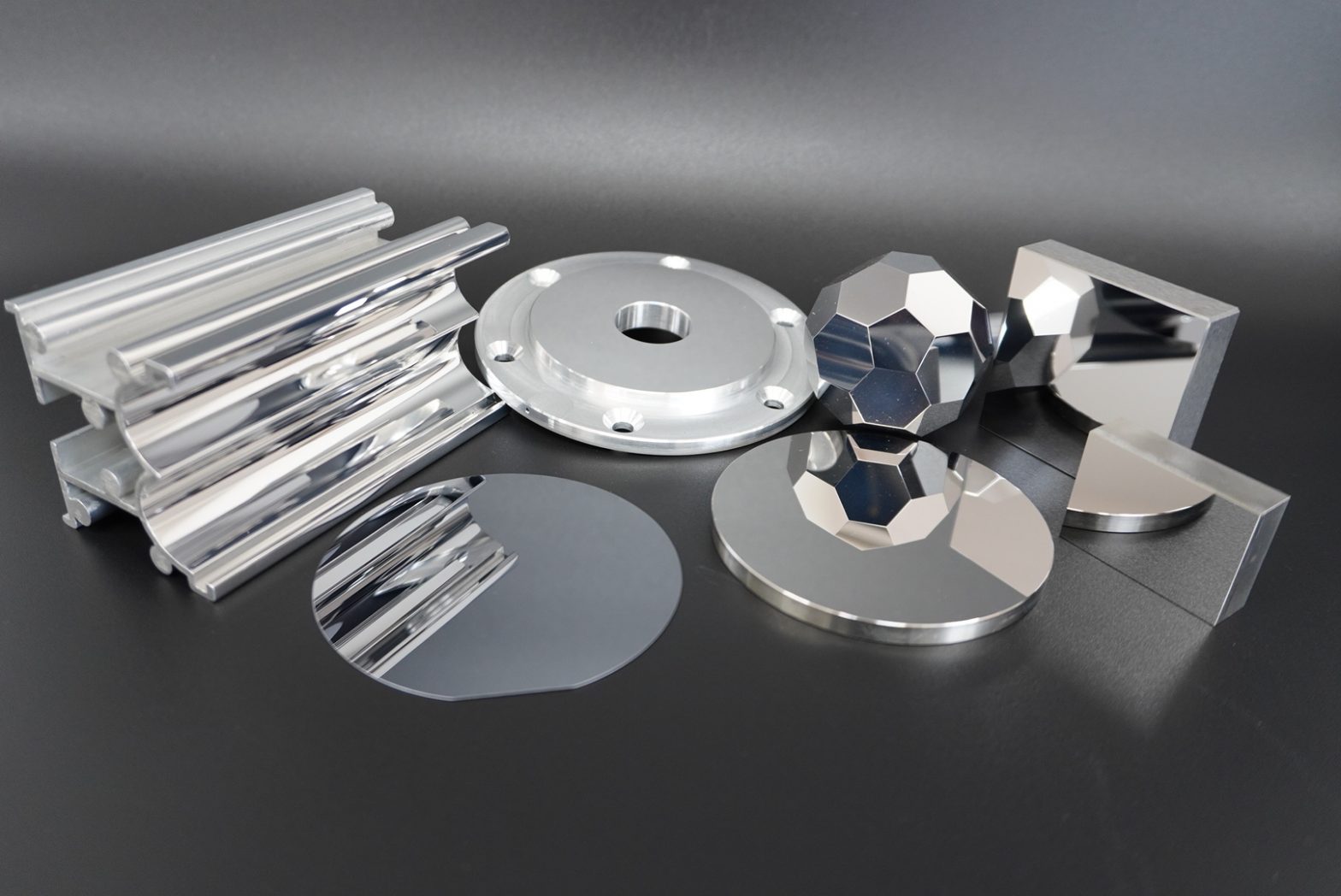
Examples of TDC’s Invar/Super Invar processing
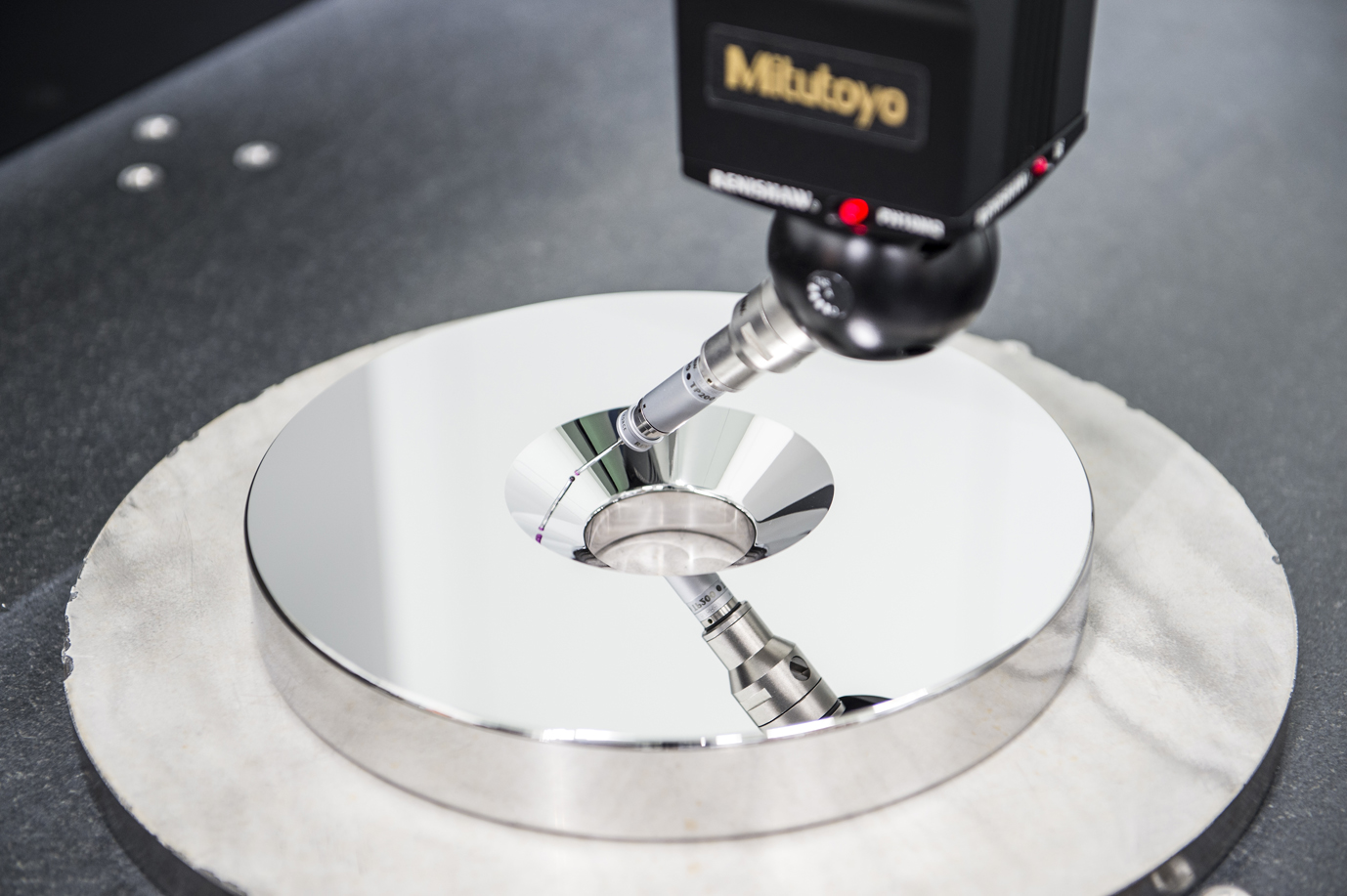
Achieving Machining Specifications
| Roughness | <0.001um |
| Flatness | <0.001mm |
| Paralellism | <0.001mm |
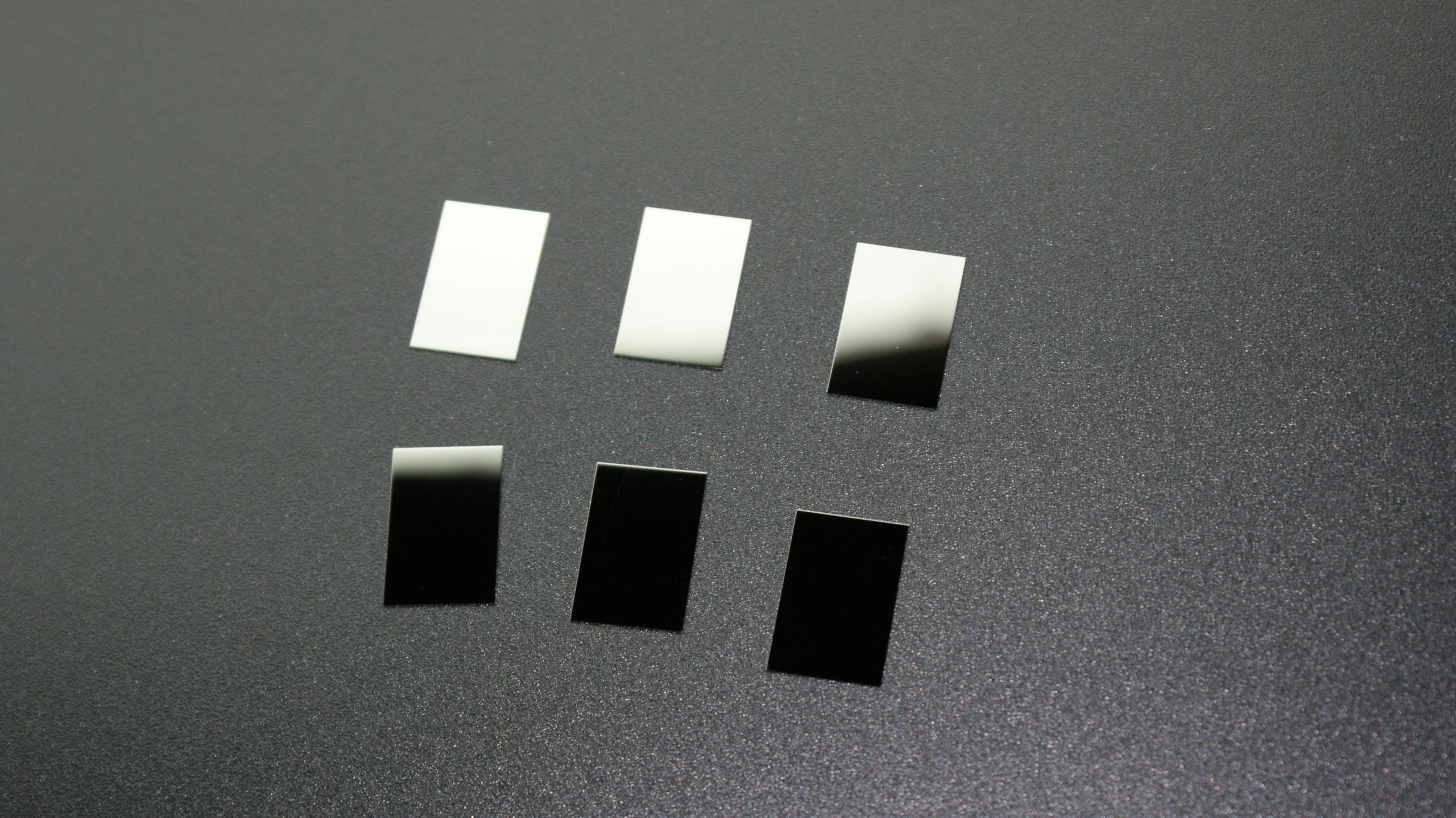
Machining example of Invar/Super Invar
We manufacture various parts, test pieces, substrates, etc. for various applications. For Invar materials, we can guarantee a surface roughness of Ra1nm or less and a flatness/parallelism of 0.001mm or less.
Please contact TDC for processing of Invar
At TDC, we are able to handle mirror-polishing of any material and precision with our know-how for processing materials and our accumulated polishing technology.
Please feel free to contact TDC for any Invar/Super Invar processing projects that have been rejected by other companies.
with nano-level precision polishing.
and production from single units to mass production.
Related page
- What is gallium nitride (GaN)? | Basic information/explanation of features and processing examples
- What is Vespel? | Vespel features and processing examples
- What is Tungsten? | Tungsten characteristics and processing examples
- Nickel
- Tantalum
- Glassy carbon (glassy carbon)
- Plate thickness and material of stainless steel plate (SUS)
- Coefficient of linear expansion
- Invar/Super Invar
- Niobium
- Hastelloy
- Engineering Plastic